HKBU Scholar’s pioneering research elucidates AI’s role in enhancing government operations and local governance
A pioneering study led by Dr Li Yiran’s team at Department of Government and International Studies of HKBU elucidates the transformative role of artificial intelligence (AI) in enhancing government operations and local governance. Titled “Making governance agile: Exploring the role of artificial intelligence in China’s local governance” , this groundbreaking research has been published in Public Policy and Administration, a top international academic journal in public administration. The project also involved a scholar from the Hong Kong Polytechnic University.
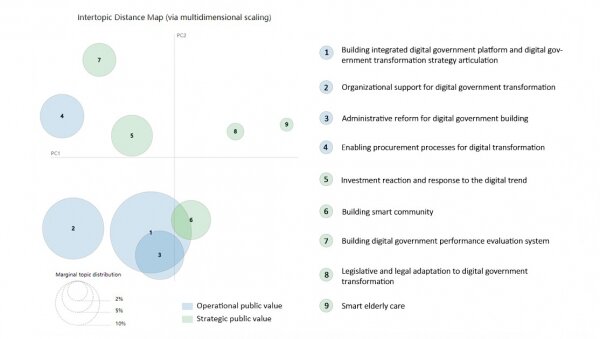
Dr Li’s team carried out a comprehensive study of AI's deployment in a pilot city in mainland China that is currently undergoing digital transformation. Their analysis highlights how AI contributes to creating public value and enhancing service delivery. The team highlighted the governments are now leveraging innovative technologies like AI to propel digital transformation and establishing “government as a platform” (GaaP). These efforts aim to fundamentally reengineer government operations, processes, and systems. As a cornerstone of the information revolution and agile governance, AI is not just autonomous but also has the ability to learn and identify patterns to make decisions. It plays a crucial role in improving the management of public agencies and has the potential to help governments deliver public services seamlessly, derive greater value from data, and achieve agility.
Dr Li’s team used a mixed-method approach combining topical modelling and qualitative analysis and found that the government prioritised operational public service related to internal benefits over strategic ones which emphasised value outside the public sector. They identified four dimensions of AI deployment in the public sector: data integration, policy innovation, smart applications, and collaborations. Dr Li’s team also illustrated two roles of AI in local governance through complex case studies – “AI cage” and “AI colleague.” AI not only increases efficiency by regulating public worker behaviours but also enhances decision-making, leading to greater agility in public service provision.
The “AI cage” refers to AI’s role in establishing a robust technology infrastructure and platform across all stages of service delivery. It helps regulate the actions of frontline workers, thereby ensuring a more consistent and reliable public service provision. On the other hand, the “AI colleague” is a more interactive aspect of AI technologies. It supports decision-making processes for frontline workers, thus enhancing the agility of public service provision. By doing so, AI enables the public sector to quickly adapt to changing circumstances and meet citizens’ needs more effectively.
This research represents a significant step in our understanding of how AI can reshape local governance. It underscores the potential of AI to drive policy innovation, integrate and analyse large volumes of data, and facilitate collaborations and smart applications, revolutionising the way public services are delivered.
Reference:
Li, Y., Fan, Y., & Nie, L. (2023). Making governance agile: Exploring the role of artificial intelligence in China’s local governance. Public Policy and Administration, 09520767231188229.